A term like R-value is well known but how many of us know what the R stands for? There are some good guesses like … Really good insulation, Reflecting heat value. The R in R-value stands for Resistance to heat flow. That's why we wear coats, hats and gloves when it's cold outside. These clothes keep us warm by trapping body heat inside our clothes, similar to how house insulation reduces heat flow in our homes.

Now that you understand that the R-value identifies how well insulation restricts heat flow, you might wonder how you can use this knowledge. These tips will help you:
Table of contents

When & Where: Increasing Insulation R-Values
When buying an existing house, you accept the insulation R-values already installed. Hopefully your home inspector will use an infrared camera for thermal imaging to identify problems in need of insulation. You can also ask the seller for a copy of their last year's heating bills, to learn how energy efficient the house is.
- When building a house, you should learn the R-values recommended by EnergyStar for the zone where you live (shared below). Local building codes may require higher R-values and you may want to negotiate higher R-values which will cost more but save you on monthly heating/cooling costs.
Note: EnergyStar new construction program requirements are much more detailed. Here's an example for Orlando, Florida … and it's easy to check the standards for your county.
- With many remodeling projects, you have the opportunity to add insulation to structures when they're open and/or will be refinished. These include exterior walls, under floors and in the attic.
- When replacing siding, it's the perfect time to add insulation to your home. Your choices include insulated vinyl siding products or rigid foam insulation which can be installed behind new siding.

What R-Value Insulation Do You Need
Energy Star specifies the R-value needed in exterior walls, attics and floors, based on where you live. First you need to identify the zone where you live using the map above. From there, you can use this table to find the recommended R-values needed to stay comfortable while minimizing your home heating/cooling costs.
For example, in central Florida where I currently live (transplanted from the northeast), these are the insulation R-values for new construction in Orlando, Florida. The table below shows that the recommendations to increase your insulation meet or exceed new construction standards.
- Most of Florida is in zone 2, with Miami and the Florida Keys are in zone 1.
- Florida “zone 2” exterior walls should have insulation that has an R-value of R-13.
- Florida “zone 2” floor insulation needs to be R-13 unless it's a slab in which case no insulation is needed.
- Florida “zone 2” ceilings need insulation that's R-30.

R-Values for Different Types of Insulation
Once you've decided it's time to add insulation to your house, the next step is researching and picking the best type of insulation for your house. Here are your choices:
- Rigid foam – is perfect if you're adding insulation to outside walls of homes, especially below grade for additions. It offers an R-value of roughly 5.0 per inch.
- Fiberglass batts – are the most common type of insulation, unrolled into the wall cavity between studs. It's used in new construction, additions and large remodeling projects where exterior walls are taken down to the studs. It's R-value is roughly 3.8 per inch.
- Blown In cellulose – is popular in remodeling projects, with holes cut in the wall to fill the open space between wall studs. It is also sprayed into the attic., providing R-3.8 per inch.
- Spray foam – is sprayed into wall cavities before drywall is installed, primarily in new construction. This insulation has an R-value of roughly 6.5 per inch. Be aware that there are several types of spray foam insulation – open cell and closed cell, so do your research carefully.

Insulation R-Values Part of A Larger System
When I ran my handyman business, many homeowners called asking us to install more insulation, but that's not always the right solution. Insulation is the easiest part of the heating/cooling system because you can see it. Here's what you need for maximum energy efficiency.
- House must be sealed, to close gaps where air can move between your home and the exterior of your house.
- The right amount of insulation should be used in the walls, attic and floors, and it must be installed properly. For example, if gaps are left airflow will increase and if insulation gets wet and/or compressed, it won't be as effective.
- Ventilation is also part of the system so that warm, moist air that does escape into your attic, can be exchanged for fresh air from outside.
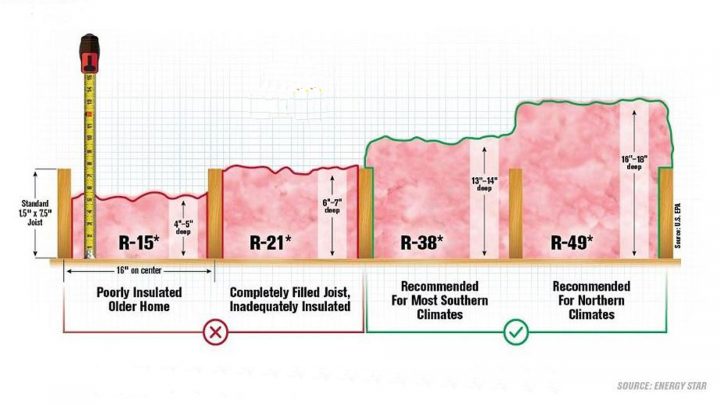
Numbers are difficult to relate to so here's an illustration showing how much attic insulation is required by today's building codes.